Published May 12, 2018. Updated April 4, 2024. Open access. | Purchase book ❯ |
Highland Snail-eating Snake (Dipsas ellipsifera)
Reptiles of Ecuador | Serpentes | Colubridae | Dipsas ellipsifera
English common name: Highland Snail-eating Snake.
Spanish common name: Caracolera altoandina.
Recognition: ♂♂ 81.0 cmMaximum distance from the snout to the tip of the tail. Snout–vent length=58.0 cm. ♀♀ 80.3 cmMaximum distance from the snout to the tip of the tail. Snout–vent length=63.0 cm..1,2 In its area of distribution, Dipsas ellipsifera is the only snake having a brownish dorsum with 27–39 blackish, vertical bars between which there is a more or less distinct narrow pale bar (Fig. 1).1,3 This species differs from Sibon dunni by having a barred color pattern (uniform brown coloration in S. dunni).3 From D. elegans, an extremely similar species restricted to west-central Ecuador, it differs by having a lower number of ventrals in both males and females.1
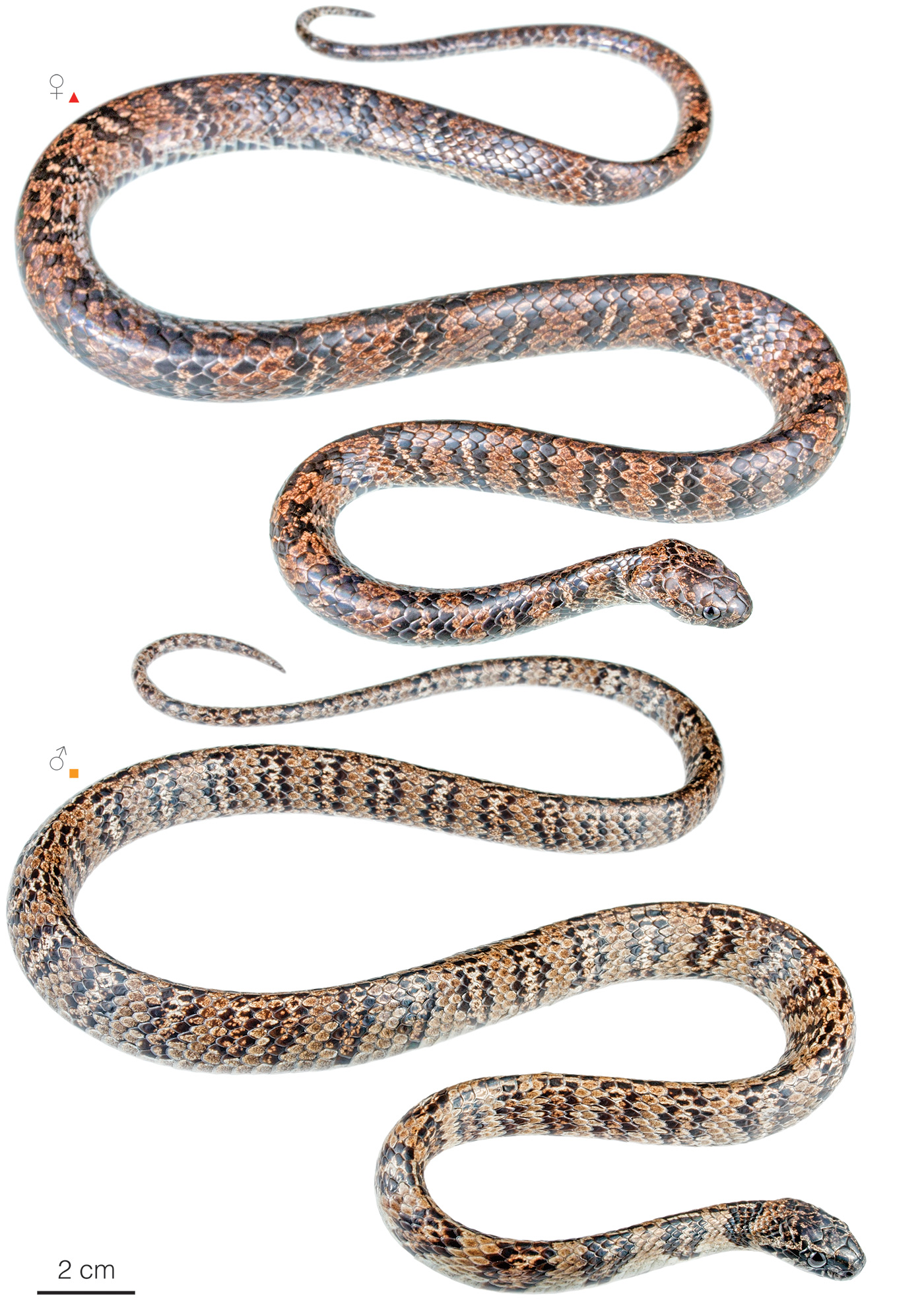

Figure 1: Individuals of Dipsas ellipsifera from Imbabura province, Ecuador: Cahuasquí (); Hacienda Zuleta ().
Natural history: Dipsas ellipsifera is a nocturnal snake that inhabits old-growth to heavily disturbed cloud forests and highland shrublands, occurring also in pastures, plantations, and urban gardens.4,5 Highland Snail-Eaters are active at night, especially if it is raining or drizzling.5 They move actively but slowly at ground level or on low shrubby vegetation.5 Nothing is known about the diet in this species, but it probably consists primarily of slugs and snails. During the day, individuals of D. ellipsifera have been found coiled under rocks.5 The typical defense mechanism of the Highland Snail-Eater consists of musking and flattening the body while expanding the head to simulate a triangular shape.5
Conservation: Endangered Considered to be facing a high risk of extinction in the near future..6 Dipsas ellipsifera is listed in this category because the species occurs as fragmented populations over a small area where more than half of the original vegetation cover has been destroyed.6 In particular, the remaining shrubland habitat along the entire Río Mira drainage is severely fragmented and declining in the extent and quality due to rural-urban expansion.6
Distribution: Dipsas ellipsifera is endemic to an area of approximately 2,727 km2 along the northwestern slopes of the Andes in Ecuador. The species also occurs in the xeric inter-Andean valley known as El Chota as well as in the more mesic upper headwaters of the Río Mira (Fig. 2).
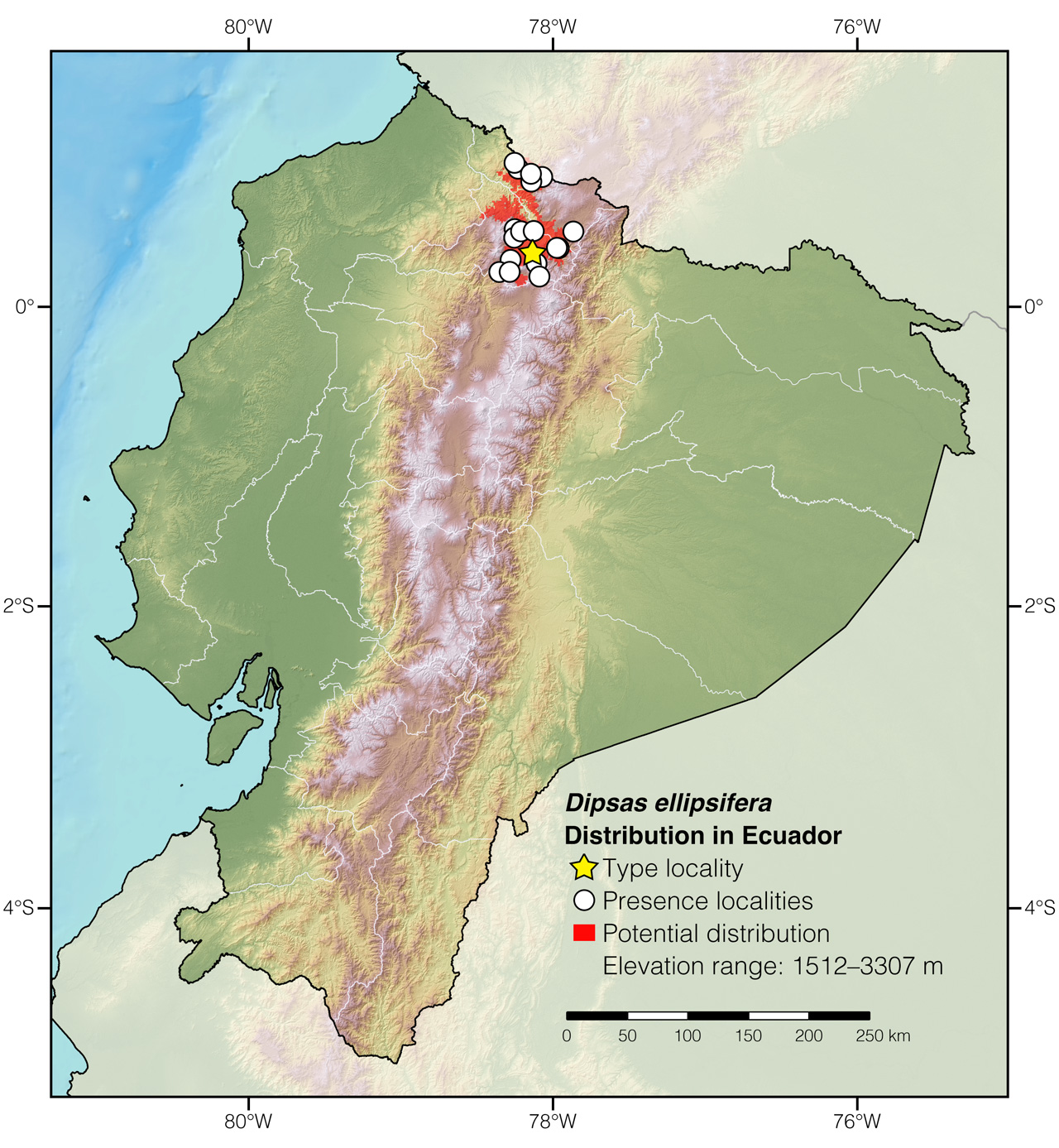
Figure 2: Distribution of Dipsas ellipsifera in Ecuador. The star corresponds to the type locality: Ibarra, Imbabura province. See Appendix 1 for a complete list of the presence localities included in the map.
Etymology: The name Dipsas comes from the Greek dipsa (=thirst)7 and probably refers to the fact that the bite of these snakes was believed to cause intense thirst. The specific epithet ellipsifera comes from the Greek word elleipsis and the Latin suffix -fero (=provided with).7 It refers to the ellipsoidal dorsal markings.
See it in the wild: Although Highland Snail-Eaters are nocturnal, they are easier to find during the day by turning over rocks in irrigated fields and pastures near remnants of native shrubland. One of the best areas to find this species is around the town Pimampiro.
Author and photographer: Alejandro ArteagaaAffiliation: Fundación Khamai, Reserva Arlequín, Ecoruta Paseo del Quinde km 56, Santa Rosa de Mindo, Pichincha 171202, Ecuador.
How to cite? Arteaga A (2024) Highland Snail-eating Snake (Dipsas ellipsifera). In: Arteaga A, Bustamante L, Vieira J (Eds) Reptiles of Ecuador: Life in the middle of the world. Available from: www.reptilesofecuador.com. DOI: 10.47051/RYMQ3386
Literature cited:
- Cadle JE (2005) Systematics of snakes in the Dipsas oreas complex (Colubridae: Dipsadinae) in western Ecuador and Peru, with revalidation of D. elegans (Boulenger) and D. ellipsifera (Boulenger). Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology 158: 67–136.
- Arteaga A, Salazar-Valenzuela D, Mebert K, Peñafiel N, Aguiar G, Sánchez-Nivicela JC, Pyron RA, Colston TJ, Cisneros-Heredia DF, Yánez-Muñoz MH, Venegas PJ, Guayasamin JM, Torres-Carvajal O (2018) Systematics of South American snail-eating snakes (Serpentes, Dipsadini), with the description of five new species from Ecuador and Peru. ZooKeys 766: 79–147. DOI: 10.3897/zookeys.766.24523
- Peters JA (1960) The snakes of the subfamily Dipsadinae. Miscellaneous Publications, Museum of Zoology, Univesity of Michigan 114: 1–224.
- Orcés VG, Almendáriz A (1987) Sistemática y distribución de las serpientes Dipsadinae del grupo oreas. Politécnica 12: 135–155.
- Field notes, Reptiles of Ecuador book project.
- Cisneros-Heredia DF, Almendáriz A, Yánez-Muñoz M (2019) Dipsas ellipsifera. The IUCN Red List of threatened species. Available from: www.iucnredlist.org. DOI: 10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T44581456A44581463.en
- Brown RW (1956) Composition of scientific words. Smithsonian Books, Washington D.C., 882 pp.
Appendix 1: Locality data used to create the distribution map of Dipsas ellipsifera in Ecuador (Fig. 2). Go to the section on symbols and abbreviations for a list of acronyms used. Asterisk (*) indicates type locality.
| Country | Province | Locality | Source |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Chilma Bajo | Arteaga et al. 2018 |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Drácula Reserve | Photo by EcoMinga |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Gruta de la Paz | Pazmiño-Otamendi & Rodríguez-Guerra 2020 |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Quebrada Golondrinas | Arteaga et al. 2018 |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Río Pailón | Arteaga et al. 2018 |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Cahuasquí | This work; Fig. 1 |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Chachimbiro | Orcés & Almendáriz 1987 |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Cotacachi | Arteaga et al. 2018 |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Hacienda Pisabo | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Hacienda Zuleta | This work; Fig. 1 |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Ibarra* | Boulenger 1898 |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Maldonado, 4 km W of | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Otavalo | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Pablo Arenas | Photo by Diego Piñán |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Pimampiro | Cadle 2005 |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Pimampiro, 1 km W of | Reptiles of Ecuador book database |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Quebrada Rumihuaico | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Río Mira | Cadle 2005 |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | UTN in Ibarra | Photo by Eduardo Obando |